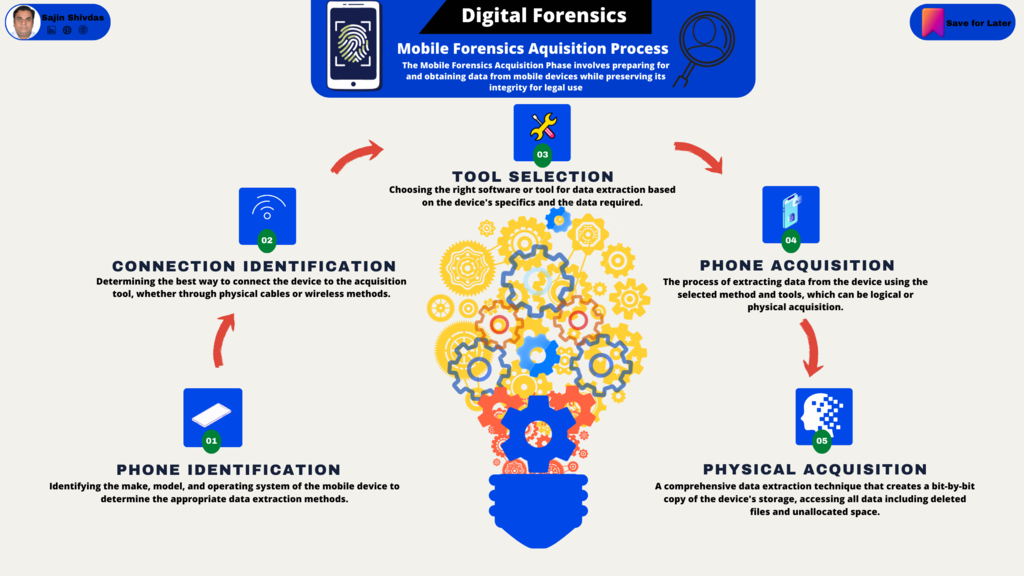
Mobile Forensics - Acquisition Process
The Mobile Acquisition Process is a series of steps used primarily in the field of digital forensics to obtain data from mobile devices. This process is crucial for law enforcement, legal investigations, and cybersecurity efforts, aiming to preserve, analyze, and present data on the device without altering it.
- Phone Identification
- Connection Identification
- Tool Selection
- Phone Acquisition
- Physical Acquisition
Mobile Forensics Acquisition Process
Phone Identification
This initial step involves identifying the make, model, and operating system (OS) of the mobile device in question. This information is critical because it determines the methods and tools that can be used for data acquisition. Different devices and operating systems have unique security features and storage mechanisms, influencing the approach to data extraction. For instance, an iPhone running iOS will have different security protocols and backup systems compared to an Android device.
Once the device's specifics are established, the next step is to identify the best method to connect the phone to the acquisition tool. This could involve physical connections (like USB, FireWire, or proprietary connectors) or wireless connections (such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth). The choice of connection depends on the device's capabilities, the data's nature, and the security measures in place. For example, a direct physical connection might be necessary for a comprehensive data extraction, but it may not be possible if the device is damaged or if the connection ports are secured.
Connection Identification
Tool Selection
After determining how to connect to the device, the next step is selecting the appropriate tool or software for data acquisition. This decision is based on the device's make, model, and operating system, as well as the type of data needed (e.g., contacts, messages, app data, etc.) and the acquisition method (logical, physical, or file system). Tools vary in their capabilities, legal compliance, and the depth of data they can extract. Popular options include Cellebrite, Oxygen Forensics, and XRY.
This step involves the actual process of acquiring data from the device using the chosen method and tools. There are generally two main types of acquisition:
Logical Acquisition: This method extracts all the logical information stored on the device, such as files and directories, without altering the device's system files. It's less invasive and quicker but may not access deleted data or encrypted partitions.
Physical Acquisition: A more comprehensive method that creates a bit-by-bit copy of the entire device, including the file system, deleted data, and unallocated space. It requires specialized tools and can bypass encryption and other security measures to access more data.
Phone Acquisition
Physical Acquisition
Although mentioned briefly in the previous step, physical acquisition deserves a deeper dive. This process involves creating an exact image of the device's storage, including all partitions and hidden sectors. It's the most thorough form of data acquisition, allowing investigators to recover deleted files, examine unallocated space, and analyze all data on the device as it existed at the time of acquisition. Physical acquisition can be challenging due to encryption, locked bootloaders, and other security features modern devices employ. Success often depends on exploiting vulnerabilities in the device's firmware or using manufacturer-specific methods to unlock the device.