Digital Forensics Process
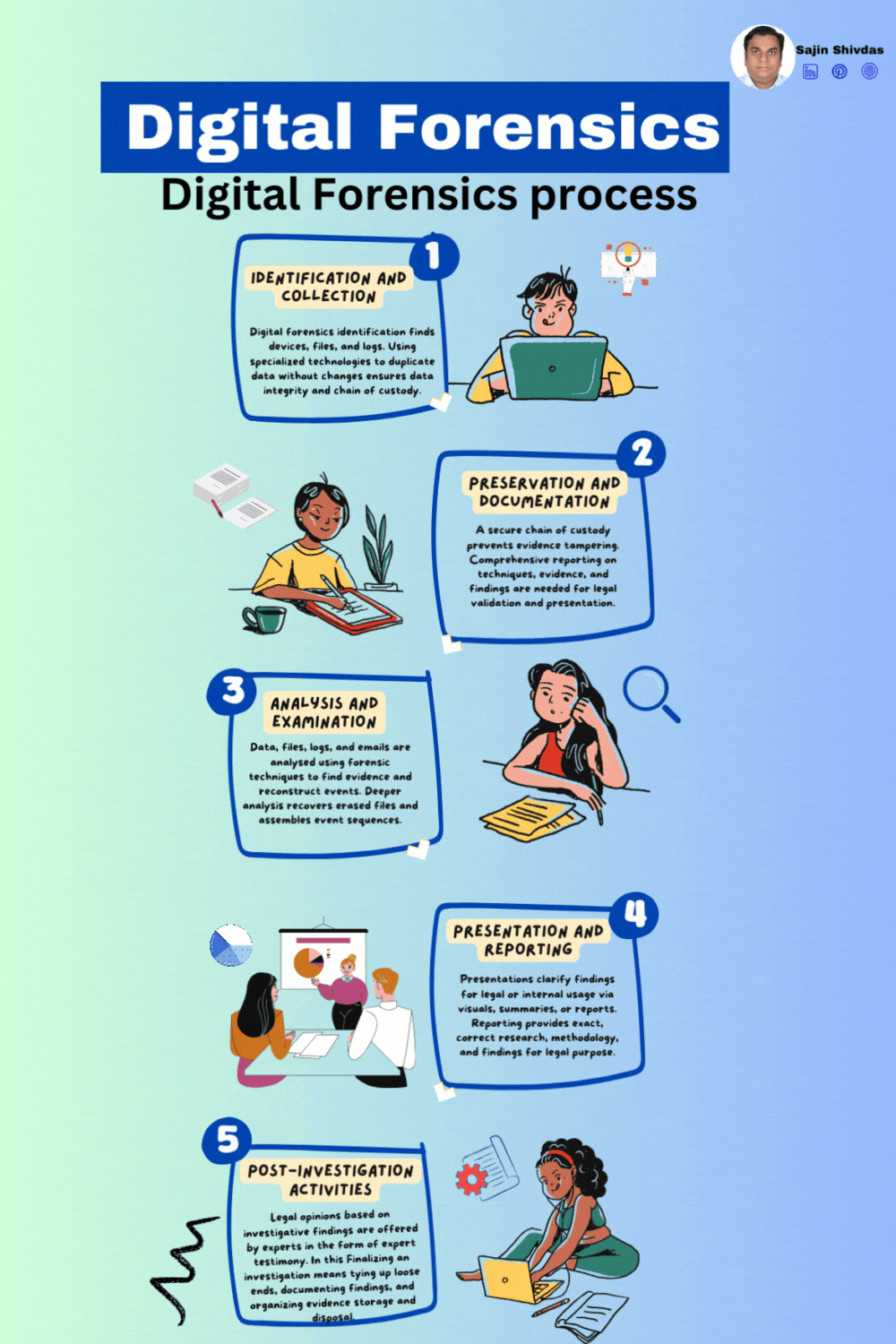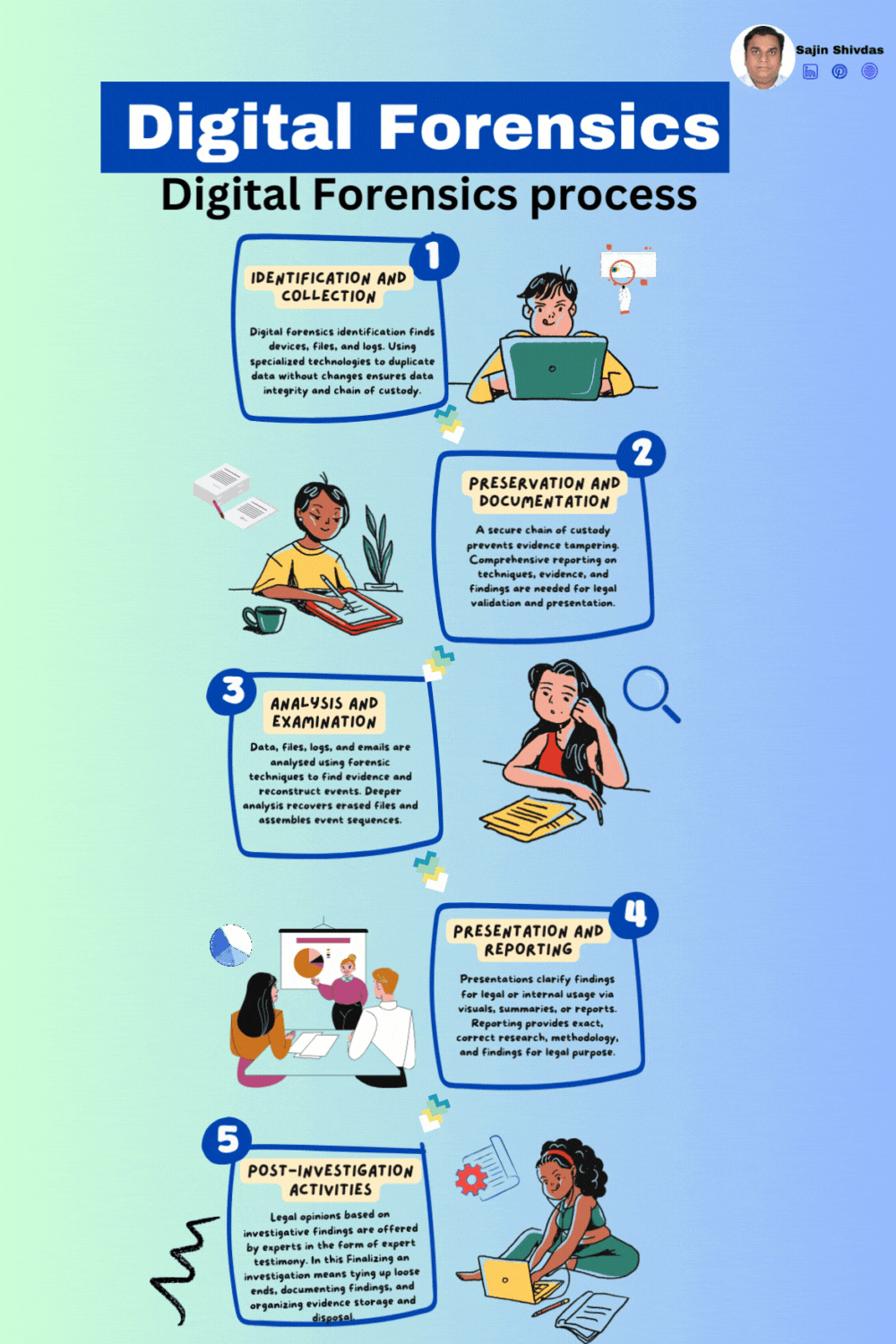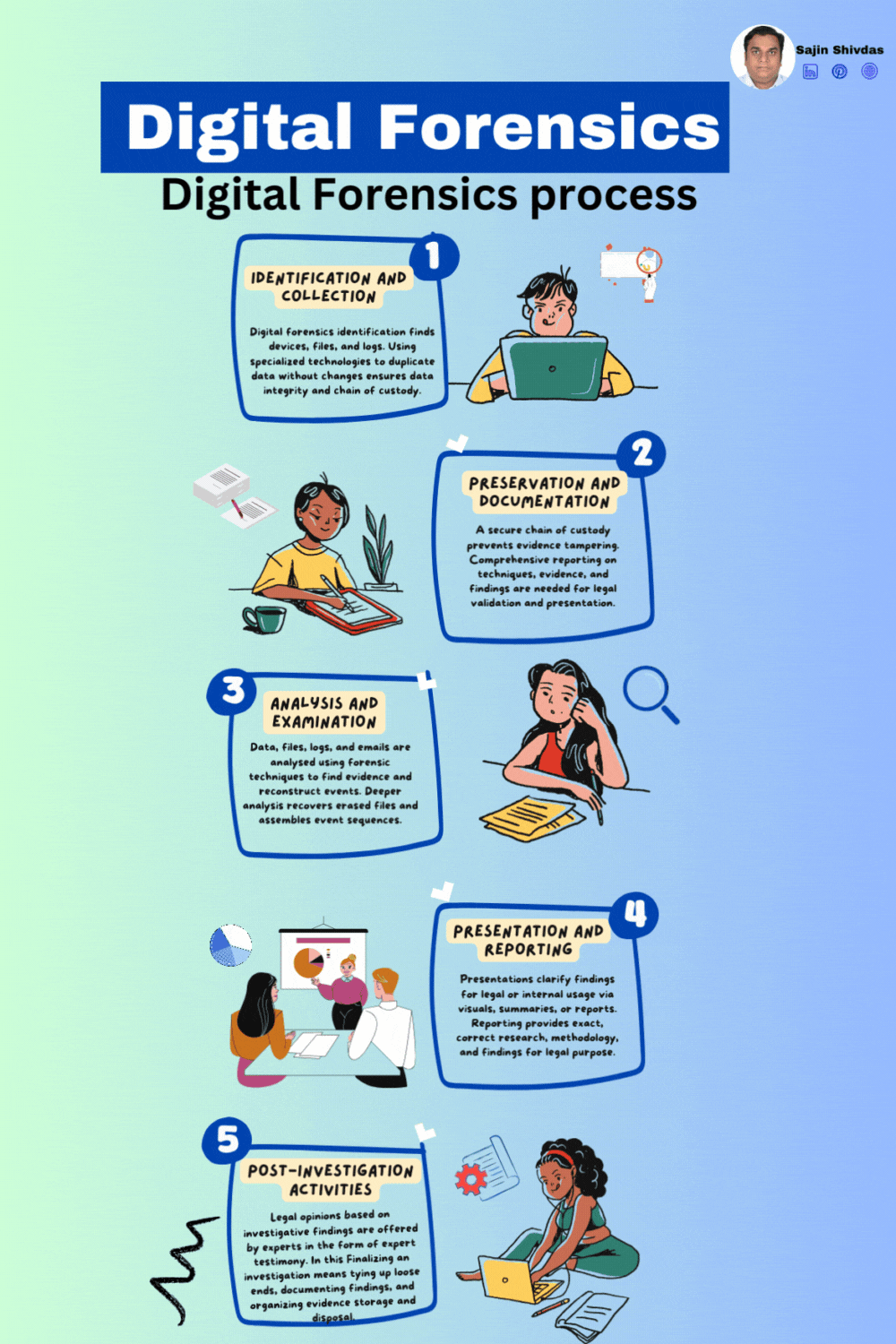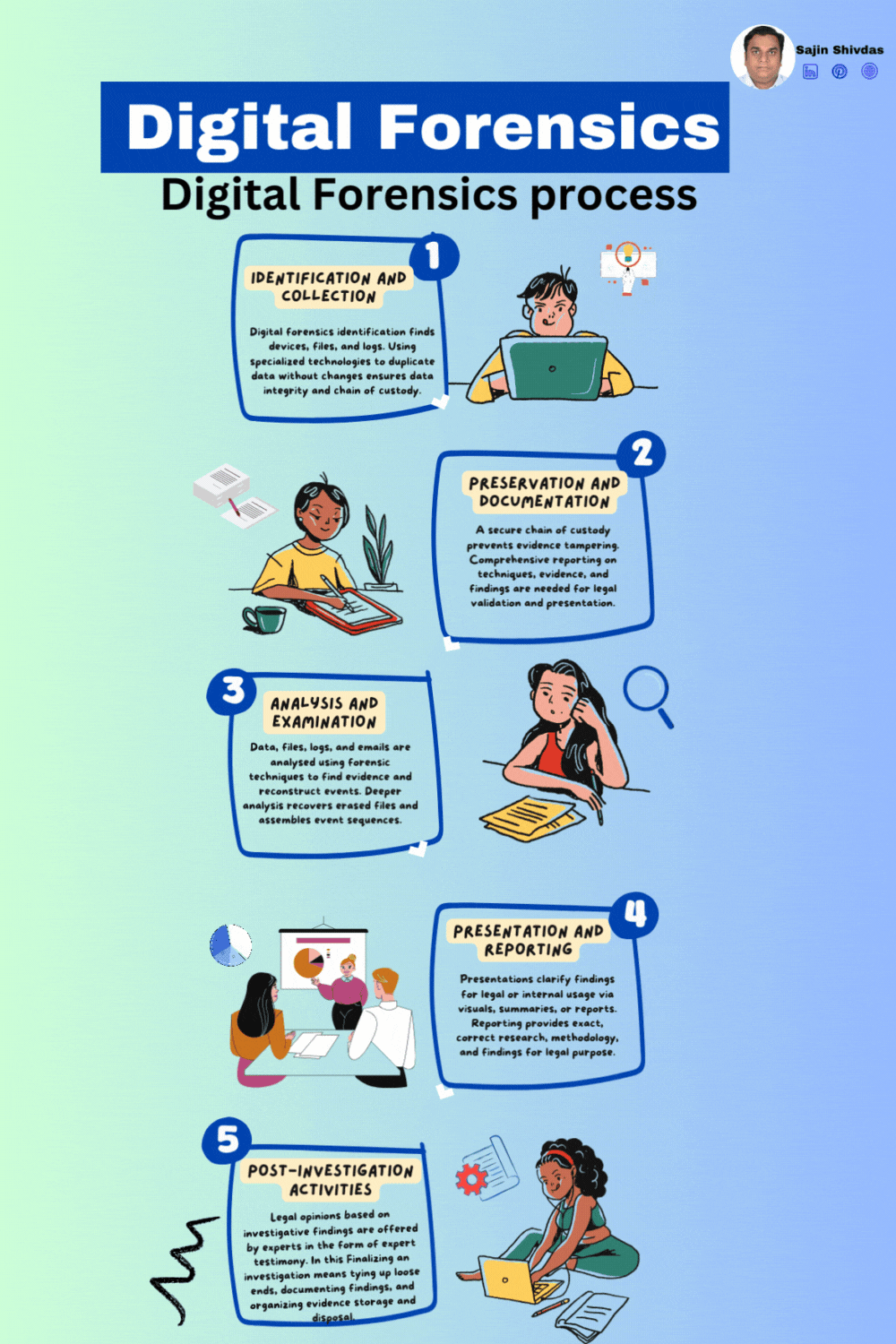
Digital forensics investigates and analyzes digital evidence to understand cybercrimes and security issues. Legal processes utilising digital evidence must follow this systematic approach to ensure its integrity and admissibility. Digital forensics requires many processes to thoroughly investigate digital evidence. This systematic approach follows a carefully designed framework from identifying and collecting prospective evidence to reporting and post-investigation actions. Digital forensics include identification, collection, preservation, documentation, analysis, examination, presentation, reporting, and post-investigation. Explore each procedure in depth. Each phase of digital artefact analysis helps resolve cyber-related incidents and legal proceedings.
Identification and Collection
Objective: Identify and collect potential digital evidence relevant to the investigation.
Activities:
• Determine the scope and objectives of the investigation.
• Identify sources of potential evidence, including devices, networks, or digital systems.
• Secure and document the crime scene to prevent contamination.
• Collect and preserve evidence using forensically sound methods, such as creating a forensic image of storage devices.
Objective: Ensure the integrity and preservation of collected evidence.
Activities:
• Create a detailed and accurate chain of custody for all collected evidence.
• Document the condition of the evidence, noting any physical or digital alterations.
• Use write-blocking mechanisms to prevent unintentional modifications to digital evidence.
• Securely store and label evidence to maintain its integrity throughout the investigation.
Objective: Analyze and examine the collected evidence to extract relevant information.
Activities:
• Use forensic tools and techniques to analyze digital evidence, such as examining file systems, recovering deleted files, or extracting metadata.
• Identify patterns, anomalies, or potential relationships within the data.
• Reconstruct events or actions that led to the creation or alteration of the evidence.
• Evaluate the credibility and relevance of the evidence in the context of the investigation.
Objective: Present findings and analysis in a clear and understandable manner.
Activities:
• Document the analysis process, detailing the methods and tools used.
• Prepare a comprehensive report summarizing key findings, methodologies, and conclusions.
• Provide context and interpretation of the digital evidence within the legal framework.
• Present the findings to stakeholders, such as law enforcement, legal teams, or other relevant parties.
Objective: Conclude the investigation and ensure proper handling of evidence.
Activities:
• Close the investigation and determine the resolution of the case.
• Properly store and archive evidence for future reference or legal proceedings.
• Document lessons learned and areas for improvement in the forensic process.
• If required, collaborate with legal authorities for potential court proceedings.