CISSP Mindmap – Domain 01
A comprehensive CISSP Mindmap Series will include all 8 Domains. This collection is designed to equip prospective CISSP professionals with essential resources for exam preparation, training and reference.
CISSP Mindmap - Domain 01
CISSP Interactive Mindmap
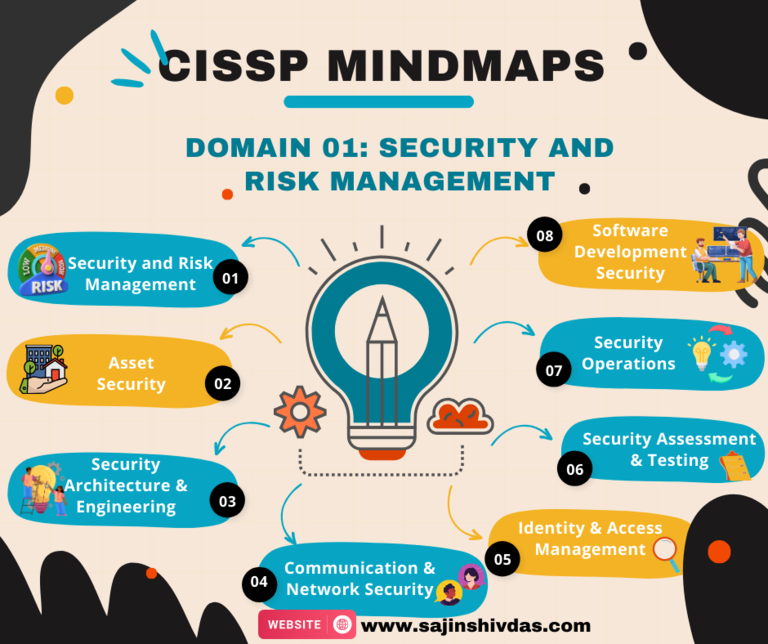
Domain_01: Key Concepts and Terminology
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals.
- Integrity: Maintaining and assuring the accuracy and completeness of data.
- Availability: Ensuring that information and resources are accessible when needed.
- Authenticity: Verification that data and communications are genuine.
- Non-repudiation: Assurance that someone cannot deny the validity of their actions.
- Asset: Anything of value to an organization (e.g., data, hardware, software).
- Threat: Potential occurrence that may cause an undesirable outcome.
- Vulnerability: Weakness in an asset that can be exploited by threats.
- Risk: The likelihood that a threat will exploit a vulnerability.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying assets, threats, and vulnerabilities to calculate risk.
- Risk Response: Strategies include mitigation, transference, avoidance, and acceptance.
- Residual Risk: Risk remaining after applying risk management strategies.
- Risk Tolerance: The level of risk an entity is willing to accept to achieve its objectives.
- Security Policies: High-level statements that define security objectives and the management framework.
- Security Control Frameworks: Common frameworks include NIST, ISO, COBIT, and PCI-DSS.
- Due Care/Due Diligence: Legal principles that require organizations to take necessary actions to protect their assets.
- Data Owner: The entity that has ultimate responsibility for data.
- Data Custodian: Responsible for implementing data protection measures.
- Security Officer: Responsible for developing and implementing security policies.
- Preventive Controls: Designed to prevent a security incident (e.g., firewalls, access controls).
- Detective Controls: Designed to detect security incidents (e.g., intrusion detection systems).
- Corrective Controls: Designed to correct or mitigate the impact of security incidents.
- Background Checks: Screening of individuals for roles within an organization.
- Onboarding/Termination Procedures: Ensuring proper access control during employee lifecycle.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees on security policies and best practices.
- Third-Party Risk: Risks associated with acquiring products and services from external suppliers.
- Minimum Security Requirements: Defining security criteria for vendors.
- NIST: Provides guidelines for risk management in federal information systems.
- ISO: International standard for information security management.
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Access control policy where the owner decides access.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access control policy based on information clearance.
- Identity and Authentication: Verification of the identity of a user, process, or device.
- Threat Vector: The path through which an attack can exploit a vulnerability.
- Threat Agent: Entity that initiates a threat action.
- Risk-Centric Approaches: Include methodologies like VAST, DREAD, PASTA, STRIDE.
- Security Principles
-
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals.
- Integrity: Maintaining and assuring the accuracy and completeness of data.
- Availability: Ensuring that information and resources are accessible when needed.
- Authenticity: Verification that data and communications are genuine.
- Non-repudiation: Assurance that someone cannot deny the validity of their actions.
- Risk Management Concepts
-
- Asset: Anything of value to an organization (e.g., data, hardware, software).
- Threat: Potential occurrence that may cause an undesirable outcome.
- Vulnerability: Weakness in an asset that can be exploited by threats.
- Risk: The likelihood that a threat will exploit a vulnerability.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying assets, threats, and vulnerabilities to calculate risk.
- Risk Response: Strategies include mitigation, transference, avoidance, and acceptance.
- Residual Risk: Risk remaining after applying risk management strategies.
- Risk Tolerance: The level of risk an entity is willing to accept to achieve its objectives.
- Security Governance
-
- Security Policies: High-level statements that define security objectives and the management framework.
- Security Control Frameworks: Common frameworks include NIST, ISO, COBIT, and PCI-DSS.
- Due Care/Due Diligence: Legal principles that require organizations to take necessary actions to protect their assets.
- Security Roles and Responsibilities
-
- Data Owner: The entity that has ultimate responsibility for data.
- Data Custodian: Responsible for implementing data protection measures.
- Security Officer: Responsible for developing and implementing security policies.
- Security Controls
-
- Preventive Controls: Designed to prevent a security incident (e.g., firewalls, access controls).
- Detective Controls: Designed to detect security incidents (e.g., intrusion detection systems).
- Corrective Controls: Designed to correct or mitigate the impact of security incidents.
- Personnel Security
-
- Background Checks: Screening of individuals for roles within an organization.
- Onboarding/Termination Procedures: Ensuring proper access control during employee lifecycle.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees on security policies and best practices.
- Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM)
-
- Third-Party Risk: Risks associated with acquiring products and services from external suppliers.
- Minimum Security Requirements: Defining security criteria for vendors.
- Risk Frameworks
-
- NIST: Provides guidelines for risk management in federal information systems.
- ISO: International standard for information security management.
- Access Control
-
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Access control policy where the owner decides access.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access control policy based on information clearance.
- Identity and Authentication: Verification of the identity of a user, process, or device.
- Threat Modeling
-
- Threat Vector: The path through which an attack can exploit a vulnerability.
- Threat Agent: Entity that initiates a threat action.
- Risk-Centric Approaches: Include methodologies like VAST, DREAD, PASTA, STRIDE.
Domain_01: Key Terms & Definitions
- Asset: Valuable resources you‟re trying to protect (people, data, systems, buildings, etc.)
- Vulnerability: A weakness in a system that allows a threat to cause harm | A gap in protection
- Threat: A potentially harmful occurrence (DoS attack, virus, tornado, power outage, etc.)
- Threat Agent: An entity acting against an asset
- Threat Vector: The medium through which a threat agent exploits a vulnerability (ex. email attachment, open port)
- Impact: The severity of the damage, usually expressed in dollars
- Exposure: An instance of being exposed to losses from a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability
- Risk: The likelihood of a threat agent leveraging an asset to act against an asset (Requires a loss)
The probability of damage occurring and the ramifications of the potential damage **Any risk involving the loss of human life is extremely high and must be mitigated** - Risk= Threat x Vulnerability | Risk= Threat x Vulnerability x Cost | Risk= Threat x Vulnerability x Impact
- Safeguard: A measure taken to reduce risk
- (TCO) Total Cost of Ownership: The cost of a safeguard (up-front cost + annual cost of maintenance)
- (ROI) Return on Investment: Money saved by deploying a safeguard (safeguards shouldn‟t cost more than asset)
- Risk Analysis: Identify assets, discover threats that put them at risk, and estimate potential loss
- Risk Decisions: Determine which safeguards we deploy to protect our assets, and the budget for doing so
- Security Governance: The organizational structure required for a successful information security program
- Least Privilege: User should be granted minimum amount of access (authorization) required to do their jobs, and no more.
- Need to Know: More granular than least privilege, and one step farther. The user must have a need to know a specific piece of information before being granted access to it.
- Defense in Depth: Layered Defense. Applying multiple controls (safeguards) to reduce risk. Any one security control may fail, so applying multiple increases the CIA of data.
Domain_01: Key Areas
- Understanding Risk management concepts
- Threat modeling concepts and processes
- Compliance , Legal, Regulatory , and Privacy
- Professional ethics – Know the ISC 2 code
- Security governance principles
- Security policies , standards , procedures and guidelines
- Business continuity requirements
- Security education, training, and awareness
Resources
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Study Guide (OSG) 9th Edition by Mike Chapple, James Michael Stewart, and Darril Gibson
- Chapter 01 – Chapter 04, Pg1-178
- CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth Editionby Fernando Maymi and Shon Harris
- Part I, Pg3-209
- Eleventh Hour CISSP® Study Guide, Third Editionby Eric Conrad, Seth Misenar, Joshua Feldma
- Domain-01, Pg1-32
- Destination Certification – A Concise Guideby Rob Witcher, John Berti, Lou Hablas, Nick Mitropoulos
- Domain-01, Pg11-69
-
The Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 6th Edition by Arthur Deane and Aaron Kraus
- Domain-01, Pg1-96
Books Reference
Practice Tests Reference
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Practice Testsby Mike Chapple and David Seidl
- How to Think Like a Manager for the CISSP Examby Luke Ahmed
- Boson Practice Exam
- Study Notes and Theory (SNT) by Luke Ahmed
Videos Reference
- Mike Chapple’sCISSP Cert Prep on LinkedIn Learning.
- Kelly Handerhan’sCISSP Prep Course on Cybrary
- Destination CISSP Mindmap Video
- Pete Zerger’s CISSP Exam Cram
- Prabh’s Coffee Shots
- Luke Ahmed’s Study Notes and Theory (SNT)
Credits & Disclaimer
We express our gratitude to the below-mentioned authors, creators, and sources which have been referred for the creation of our Interactive CISSP Mindmap –Mike Chapple and David Seidl (OSG), Luke Ahmed (SNT), Pete Zerger (Exam Cram), Prashant Mohan (Memory Palace) , Prabh (Coffee shots), Rob Witcher (destcert.com/) and M. Waleed Khaliq (CISSP Concepts Guide).This Mindmap has been meticulously created to ensure that information is shared effectively. This Mindmap aims to offer a thorough grasp of essential concepts with a dedication to assist enhanced learning experiences. We hope that this resource helps people absorb information more thoroughly, which will lead to a broader understanding of each CISSP domains and is freely available for all.
Contribution
We have already included some reference images and short notes for most of the topics so that users can more effectively refer to the content in the mindmap. If you have any information, images, or notes that can make the mindmap more effective, please feel free to share them.
https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/tree/main/CISSP_Domain_01
For issues and concern please feel free to raise a issue in Github link https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/issues
Connect with me www.linkedin.com/in/sajin-shivdas
Related Mindmaps
Find the related mindmaps of CISSP Domains below.