CISSP Mindmap-Domain 6: Security Assessment and Testing
An Interactive CISSP Mindmap Series
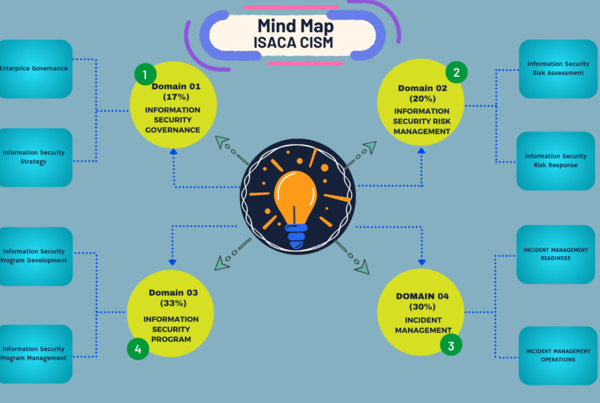
CISSP Mindmap – Domain 06
A comprehensive CISSP Mindmap Series will include all 8 Domains. This collection is designed to equip prospective CISSP professionals with essential resources for exam preparation, training and reference.
CISSP Mindmap - Domain 06
CISSP Interactive Mindmap
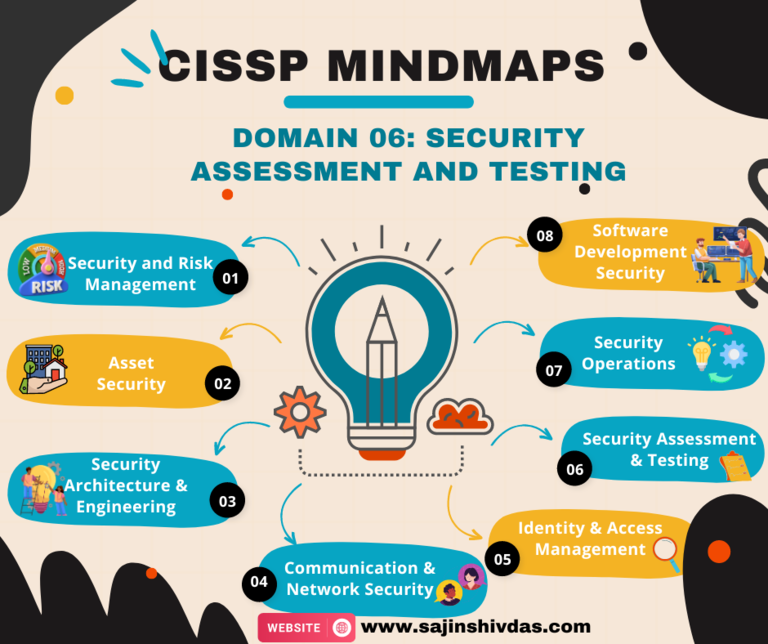
Domain_06: Key Concepts and Terminology
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifies security weaknesses in a system, network, or application.
- Penetration Testing: Simulates real-world attacks to test the effectiveness of security controls.
- Security Audits: Formal reviews of security policies, procedures, and controls.
- Log Reviews: The process of examining logs to identify security incidents, policy violations, or operational issues.
- Code Review: Systematic examination of source code to find and fix security vulnerabilities.
- White-box Testing: The tester has full knowledge of the system, including architecture, source code, and documentation.
- Black-box Testing: The tester has no prior knowledge of the system’s internal workings.
- Gray-box Testing: The tester has partial knowledge of the system.
- Authenticated Scans: Performed with system access to find more detailed vulnerabilities.
- Unauthenticated Scans: Performed without system access, identifying vulnerabilities visible to an outside attacker.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Tools used to identify known vulnerabilities (e.g., Nessus, OpenVAS).
- Port Scanners: Scan network ports to find open and potentially vulnerable services (e.g., Nmap).
- Web Vulnerability Scanners: Used to find vulnerabilities specific to web applications (e.g., SQL injection, XSS).
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network traffic for malicious activities or policy violations.
- Continuous Monitoring: An ongoing process to detect, analyze, and respond to security risks.
- Risk Assessment: Identifies and evaluates potential risks to information systems.
- Security Control Testing: Ensures that security controls are implemented correctly and are effective.
- Compliance Testing: Validates adherence to industry standards, regulations, and policies.
- Static Testing: Examines code and system components without executing them (e.g., code reviews, static analysis tools).
- Dynamic Testing: Tests the system or application during runtime (e.g., penetration testing, dynamic analysis tools).
- Tabletop Exercises: Discussion-based sessions where team members talk through a simulated security incident.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): The average time it takes to identify a security incident.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): The average time taken to respond to and mitigate a security incident.
- False Positives/Negatives: Metrics used to measure the accuracy of detection tools.
- SOC Reports: Service Organization Control reports evaluate the effectiveness of an organization’s internal controls.
- Common Criteria: An international standard for evaluating the security properties of IT products.
- Certification and Accreditation (C&A): A process that ensures a system meets specific security standards before it is deemed operational.
- Use of Sandboxing: Running code in a controlled environment to analyze its behavior without risking the main system.
- Test Data Management: Using masked or synthetic data during testing to protect sensitive information.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating systems to address identified vulnerabilities.
- Assessment and Testing Techniques
-
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifies security weaknesses in a system, network, or application.
- Penetration Testing: Simulates real-world attacks to test the effectiveness of security controls.
- Security Audits: Formal reviews of security policies, procedures, and controls.
- Log Reviews: The process of examining logs to identify security incidents, policy violations, or operational issues.
- Code Review: Systematic examination of source code to find and fix security vulnerabilities.
- Testing Types
-
- White-box Testing: The tester has full knowledge of the system, including architecture, source code, and documentation.
- Black-box Testing: The tester has no prior knowledge of the system’s internal workings.
- Gray-box Testing: The tester has partial knowledge of the system.
- Authenticated Scans: Performed with system access to find more detailed vulnerabilities.
- Unauthenticated Scans: Performed without system access, identifying vulnerabilities visible to an outside attacker.
- Key Testing Tools
-
- Vulnerability Scanners: Tools used to identify known vulnerabilities (e.g., Nessus, OpenVAS).
- Port Scanners: Scan network ports to find open and potentially vulnerable services (e.g., Nmap).
- Web Vulnerability Scanners: Used to find vulnerabilities specific to web applications (e.g., SQL injection, XSS).
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network traffic for malicious activities or policy violations.
- Assessment Concepts
-
- Continuous Monitoring: An ongoing process to detect, analyze, and respond to security risks.
- Risk Assessment: Identifies and evaluates potential risks to information systems.
- Security Control Testing: Ensures that security controls are implemented correctly and are effective.
- Compliance Testing: Validates adherence to industry standards, regulations, and policies.
- Testing Methodologies
-
- Static Testing: Examines code and system components without executing them (e.g., code reviews, static analysis tools).
- Dynamic Testing: Tests the system or application during runtime (e.g., penetration testing, dynamic analysis tools).
- Tabletop Exercises: Discussion-based sessions where team members talk through a simulated security incident.
- Key Metrics and Measurements
-
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): The average time it takes to identify a security incident.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR): The average time taken to respond to and mitigate a security incident.
- False Positives/Negatives: Metrics used to measure the accuracy of detection tools.
- Security Auditing and Evaluation
-
- SOC Reports: Service Organization Control reports evaluate the effectiveness of an organization’s internal controls.
- Common Criteria: An international standard for evaluating the security properties of IT products.
- Certification and Accreditation (C&A): A process that ensures a system meets specific security standards before it is deemed operational.
- Testing Best Practices
-
- Use of Sandboxing: Running code in a controlled environment to analyze its behavior without risking the main system.
- Test Data Management: Using masked or synthetic data during testing to protect sensitive information.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating systems to address identified vulnerabilities.
Domain_06: Key Terms & Definitions
Vulnerability Assessment: The process of identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing (or ranking) the vulnerabilities in a system.
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing): An authorized simulated attack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system.
Security Audits: A comprehensive review of an organization’s adherence to regulatory guidelines. Audits assess the strength and thoroughness of compliance preparations, security policies, user access controls, and risk management procedures over the course of a compliance audit.
Security Assessment: The process of determining how effectively an entity being assessed meets specific security criteria. It’s broader than testing and includes risk assessment, vulnerability assessment, and penetration testing.
Risk Assessment: The process of identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing (or ranking) the risks to an organization’s information assets. This helps to determine the appropriate management action and priorities for managing information security risks.
Code Review: The systematic examination of computer source code intended to find and fix mistakes overlooked in the initial development phase, improving both the overall quality of software and the developers’ skills.
Compliance Testing: Verifying that the controls are in place and are being maintained according to the applicable policies, procedures, or regulations.
Security Posture Assessment: An evaluation to determine the security state of an information system or network, based on information system security controls and procedures.
Incident Response Testing: Testing an organization’s incident response capabilities to ensure that, in the event of a security breach or downtime, the necessary steps can be taken to quickly and effectively manage the situation.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Identifies the effects of disruption of business functions and processes. It also helps in developing strategies and plans for mitigating the impact.
Security Control Testing: Testing and evaluating the effectiveness of security controls (safeguards or countermeasures) to detect, prevent, respond to, or mitigate security risks to an information system.
Domain_06: Key Areas
Assessment and Test Strategies
- Understanding and implementing strategies to assess the effectiveness of security controls and mechanisms within an information system.
- Developing and managing a security assessment plan.
Security Process Data (e.g., management and operational controls)
- Analyzing and assessing the data related to security processes to ensure they are functioning as intended.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of management and operational controls in meeting security requirements.
Security Control Testing
- Techniques and methods for testing security controls to validate their effectiveness.
- Includes vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, log reviews, synthetic transactions, code review and testing, and misuse case testing.
Test Outputs (e.g., automated, manual)
- Understanding the outputs from various testing methods, including both automated tools and manual testing procedures.
- Analyzing test results to identify security weaknesses and non-compliance with security policies.
Security Architectures Vulnerabilities
- Identifying and assessing vulnerabilities within security architectures.
- Understanding common vulnerabilities in network, system, application architectures, and how to mitigate them.
Vulnerability Assessment
- Conducting assessments to identify vulnerabilities in information systems.
- Utilizing various tools and techniques for vulnerability identification.
Penetration Testing
- Planning and conducting penetration tests to simulate attacks on systems or networks to evaluate their defenses.
- Understanding the difference between white box, black box, and gray box testing.
Log Reviews
- Regularly reviewing logs to detect unauthorized access or activities, security incidents, and to ensure that security controls are functioning correctly.
Synthetic Transactions
- Performing simulated transactions to test system performance and security in a controlled environment.
Code Review and Testing
- Reviewing and testing code for security vulnerabilities, compliance with coding standards, and security best practices.
Misuse Case Testing
- Testing systems against misuse cases to identify potential security breaches or failures.
Test Coverage Analysis
- Analyzing test coverage to ensure that all parts of the application or system have been tested for vulnerabilities.
Security Audits
- Conducting formal audits to assess the compliance of systems and processes with established security policies and standards.
Resources
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Study Guide (OSG) 9th Edition by Mike Chapple, James Michael Stewart, and Darril Gibson
- Chapter 15, Pg723-759
- CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth Editionby Fernando Maymi and Shon Harris
- Part VI, Pg813-881
- Eleventh Hour CISSP® Study Guide, Third Editionby Eric Conrad, Seth Misenar, Joshua Feldma
- Domain-06, Pg135-144
- Destination Certification – A Concise Guideby Rob Witcher, John Berti, Lou Hablas, Nick Mitropoulos
- Domain-06, Pg349-382
-
The Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 6th Edition by Arthur Deane and Aaron Kraus
- Domain-06, Pg419-548
Books Reference
Practice Tests
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Practice Testsby Mike Chapple and David Seidl
- How to Think Like a Manager for the CISSP Examby Luke Ahmed
- Boson Practice Exam
- Study Notes and Theory (SNT) by Luke Ahmed
Videos
- Mike Chapple’sCISSP Cert Prep on LinkedIn Learning.
- Kelly Handerhan’sCISSP Prep Course on Cybrary
- Destination CISSP Mindmap Video
- Pete Zerger’s CISSP Exam Cram
- Prabh’s Coffee Shots
- Luke Ahmed’s Study Notes and Theory (SNT)
Credits & Disclaimer
We express our gratitude to the below-mentioned authors, creators, and sources which have been referred for the creation of our Interactive CISSP Mindmap –Mike Chapple and David Seidl (OSG), Luke Ahmed (SNT), Pete Zerger (Exam Cram), Prashant Mohan (Memory Palace) , Prabh (Coffee shots), Rob Witcher (destcert.com/) and M. Waleed Khaliq (CISSP Concepts Guide).This Mindmap has been meticulously created to ensure that information is shared effectively. This Mindmap aims to offer a thorough grasp of essential concepts with a dedication to assist enhanced learning experiences. We hope that this resource helps people absorb information more thoroughly, which will lead to a broader understanding of each CISSP domains and is freely available for all.
Contribution
We have already included some reference images and short notes for most of the topics so that users can more effectively refer to the content in the mindmap. If you have any information, images, or notes that can make the mindmap more effective, please feel free to share them.
https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/tree/main/CISSP_Domain_06
For issues and concern please feel free to raise a issue in Github link https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/issues
Connect with me www.linkedin.com/in/sajin-shivdas
Related Mindmaps
Find the related mindmaps of CISSP Domains below.