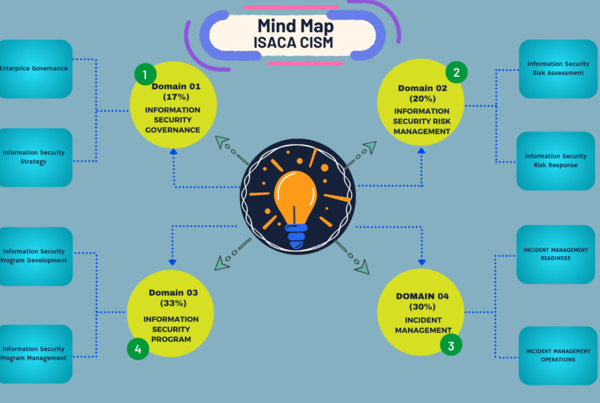
CISM Mindmap-Domain 2: Information Security Risk Management
An Interactive CISM Mindmap Series
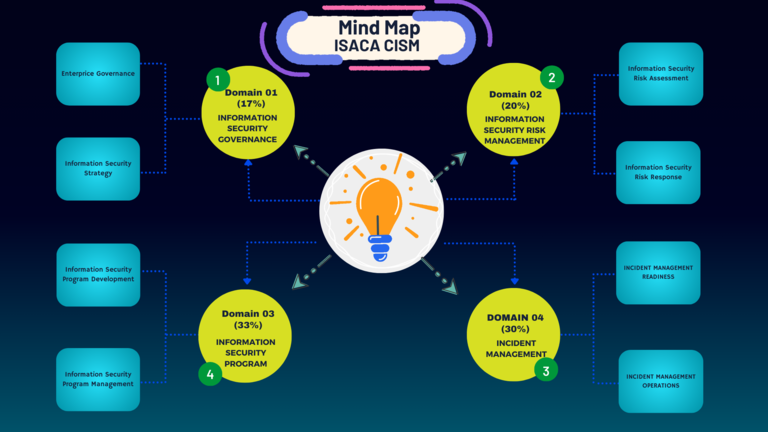
CISM Mindmap – Domain 02
CISM Mindmap Series will include all 4 Domains. This collection is designed to equip prospective CISM aspirants with essential resources for exam preparation, training and reference.
CISM Domain_02: Key Terms & Definitions
- Risk Assessment: The process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks. It is foundational in determining the extent of the potential threats and the risk they pose to the organization.
- Risk Mitigation: Actions taken to reduce the likelihood and/or impact of a risk. This could include implementing controls, adopting new policies, or changing existing procedures.
- Risk Transfer: The process of shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing. This does not eliminate the risk but rather allocates the impact to another entity.
- Risk Acceptance : The decision to accept the risk as it is, typically because the cost of mitigating the risk would exceed the benefit gained from such actions.
- Risk Avoidance: Actions taken to avoid the risk entirely, often by not engaging in activities that would generate the risk.
- Vulnerability Assessment: A systematic examination of an information system or product to determine the adequacy of security measures, identify security deficiencies, and predict effectiveness of proposed security measures.
- Threat Landscape: An overview of the types of threats an organization faces, including the tactics, techniques, and procedures used by threat actors against specific industries or entities.
- Impact Analysis: The process of analyzing the consequences of an identified risk eventuating, and determining its impact on business operations.
- Control Environment: The overall atmosphere, attitude, awareness, and actions of directors, management, and personnel regarding the internal control system and its importance to the entity. This environment serves as the foundation for effective risk management.
- Inherent Risk: The level of risk inherent in a process or environment, without considering the effect of any risk controls. It represents the baseline risk that exists before any mitigative actions are taken.
- Residual Risk: The level of risk that remains after controls are applied. Understanding residual risk is crucial for deciding whether additional measures are needed or if the remaining risk is acceptable.
- Risk Appetite: The amount and type of risk an organization is willing to take in order to meet their strategic objectives. Risk appetite is a guide to risk management decisions and helps align risks with strategy.
- Risk Tolerance: The acceptable variation an organization is willing to withstand around specific business objectives or risks. It often quantifies the acceptable limit or boundary of risk appetite.
- Security Posture: The overall security status of an organization’s software, hardware, services, networks, information, and physical premises, as well as the efficacy of the controls in place to protect from threats.
- Risk Register: A tool used to track risks and their status throughout the risk management process. It typically includes details on risk assessment, risk response plans, and current risk status.
CISM Domain_02: Key Areas
Risk Assessment:
- Identifying and evaluating risk to the organization’s assets to determine the likelihood and impact of potential security incidents.
- Utilizing various methodologies to assess risk.
Risk Response:
- Determining appropriate ways to handle identified risks, including avoidance, mitigation, sharing, and acceptance.
- Developing and implementing risk management strategies.
Risk Monitoring and Reporting:
- Continuously monitoring risk and the effectiveness of the risk management strategies.
- Reporting on risk and changes to senior management to facilitate decision-making.
Information Resource Valuation:
- Assigning value to information resources based on their importance to the business objectives and risk management strategy.
Risk Management Integration with Enterprise Risk Management (ERM):
- Ensuring that information security risk management aligns with the organization’s broader risk management practices and business goals.
Risk Management Frameworks and Methodologies:
- Utilizing established frameworks and methodologies (such as ISO 31000, NIST SP 800-30) for a systematic and structured risk management process.
Resources
- CISM® Certified Information Security ManagerStudy Guide by Mike Chapple
- CISM Certified Information Security Manager All-in-One Exam Guide, Second Edition, 2nd Editionby Peter H. Gregory
Contribution
We have already included some reference images and short notes for most of the topics so that users can more effectively refer to the content in the mindmap. If you have any information, images, or notes that can make the mindmap more effective, please feel free to share them.
https://github.com/ShivdaSaj/CISM_Interactive_Mindmap
For issues and concern please feel free to raise a issue in Github link https://github.com/ShivdaSaj/CISM_Interactive_Mindmap/issues
Connect with me www.linkedin.com/in/sajin-shivdas