CISSP Mindmap – Domain 04
A comprehensive CISSP Mindmap Series will include all 8 Domains. This collection is designed to equip prospective CISSP professionals with essential resources for exam preparation, training and reference.
CISSP Mindmap - Domain 04
CISSP Interactive Mindmap
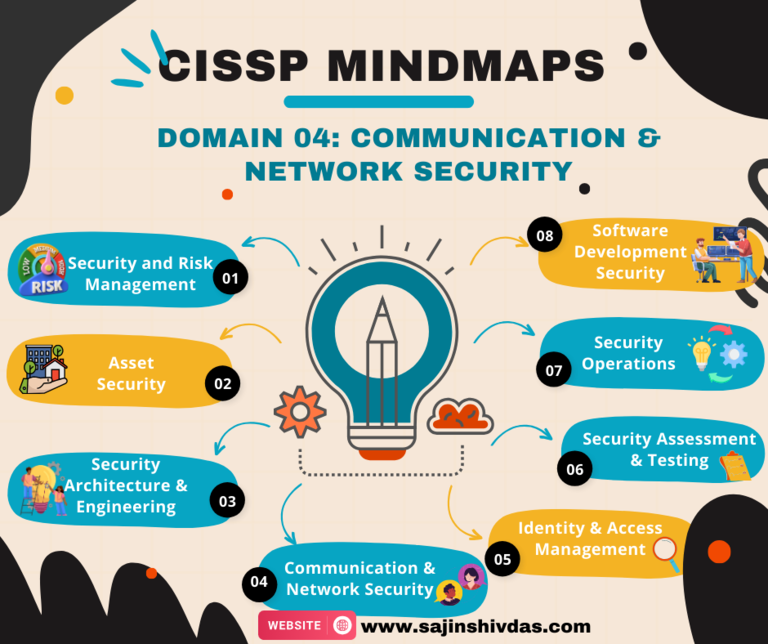
Domain_04: Key Concepts and Terminology
- OSI Model: The seven-layer model (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application) that standardizes networking functions.
- TCP/IP Model: A four-layer model (Network Interface, Internet, Transport, Application) that describes the suite of protocols used for the Internet.
- Network Topologies: The physical or logical arrangement of network devices (e.g., bus, star, ring, mesh).
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): A network segment that separates an internal network from untrusted external networks.
- Subnetting: Dividing a network into smaller, manageable segments.
- VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): Segmentation of network traffic to improve performance and security.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable data transfer.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A connectionless protocol that offers faster transmission but without guaranteed delivery.
- IP (Internet Protocol): Responsible for addressing and routing packets of data so they can travel across networks and arrive at the correct destination.
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): Used for network diagnostics, such as the “ping” command.
- Firewall: A network security device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security policies.
- IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System): IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity, while IPS actively blocks detected threats.
- Proxy Server: Acts as an intermediary for requests between clients and servers to provide filtering, logging, and content caching.
- Load Balancer: Distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed.
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2): A security protocol that provides stronger data protection and network access control in Wi-Fi networks.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): An outdated and vulnerable wireless security protocol.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): The name assigned to a Wi-Fi network.
- MAC Filtering: A security measure that limits access to a network based on the MAC addresses of client devices.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Provides secure remote access by encrypting traffic between a user’s device and the organization’s network.
- RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service): A protocol for remote user authentication and accounting.
- TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security / Secure Sockets Layer): Protocols for establishing secure communications over a computer network.
- Encryption: Techniques for protecting data in transit, such as TLS, SSL, and IPsec.
- IPsec (Internet Protocol Security): A suite of protocols for securing internet communications through authenticating and encrypting each IP packet.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): An extension of HTTP for secure communication over a computer network.
- SSH (Secure Shell): A protocol that provides secure command-line access to remote systems.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attack: Overwhelming a network or service with excessive traffic to disrupt normal operations.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: An attacker intercepts communication between two systems to eavesdrop or alter data.
- Spoofing: Faking the identity of a sender in communication to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Sniffing: Capturing and analyzing network packets to intercept sensitive data.
- 802.1X: A network access control protocol that provides authentication mechanisms for devices attempting to connect to a network.
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting): Framework for controlling access to network resources, tracking user activities, and managing user policies.
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Systems that provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): Used for managing and monitoring network devices.
- Log Analysis: Reviewing logs to identify and analyze network anomalies and security events.
- SDN (Software-Defined Networking): An approach to network management that allows dynamic, programmatically efficient network configuration.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): A private cloud environment within a public cloud infrastructure, providing isolated network resources.
- Network Architecture and Design
-
- OSI Model: The seven-layer model (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application) that standardizes networking functions.
- TCP/IP Model: A four-layer model (Network Interface, Internet, Transport, Application) that describes the suite of protocols used for the Internet.
- Network Topologies: The physical or logical arrangement of network devices (e.g., bus, star, ring, mesh).
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): A network segment that separates an internal network from untrusted external networks.
- Subnetting: Dividing a network into smaller, manageable segments.
- VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): Segmentation of network traffic to improve performance and security.
- Transmission Protocols
-
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable data transfer.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A connectionless protocol that offers faster transmission but without guaranteed delivery.
- IP (Internet Protocol): Responsible for addressing and routing packets of data so they can travel across networks and arrive at the correct destination.
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): Used for network diagnostics, such as the “ping” command.
- Network Security Devices
-
- Firewall: A network security device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security policies.
- IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System): IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity, while IPS actively blocks detected threats.
- Proxy Server: Acts as an intermediary for requests between clients and servers to provide filtering, logging, and content caching.
- Load Balancer: Distributes network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed.
- Wireless Security
-
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2): A security protocol that provides stronger data protection and network access control in Wi-Fi networks.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): An outdated and vulnerable wireless security protocol.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): The name assigned to a Wi-Fi network.
- MAC Filtering: A security measure that limits access to a network based on the MAC addresses of client devices.
- Remote Access
-
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Provides secure remote access by encrypting traffic between a user’s device and the organization’s network.
- RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service): A protocol for remote user authentication and accounting.
- TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security / Secure Sockets Layer): Protocols for establishing secure communications over a computer network.
- Secure Network Communications
-
- Encryption: Techniques for protecting data in transit, such as TLS, SSL, and IPsec.
- IPsec (Internet Protocol Security): A suite of protocols for securing internet communications through authenticating and encrypting each IP packet.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): An extension of HTTP for secure communication over a computer network.
- SSH (Secure Shell): A protocol that provides secure command-line access to remote systems.
- Threats to Network Security
-
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attack: Overwhelming a network or service with excessive traffic to disrupt normal operations.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: An attacker intercepts communication between two systems to eavesdrop or alter data.
- Spoofing: Faking the identity of a sender in communication to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Sniffing: Capturing and analyzing network packets to intercept sensitive data.
- Network Access Control (NAC)
-
- 802.1X: A network access control protocol that provides authentication mechanisms for devices attempting to connect to a network.
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting): Framework for controlling access to network resources, tracking user activities, and managing user policies.
- Network Management and Monitoring
-
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Systems that provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): Used for managing and monitoring network devices.
- Log Analysis: Reviewing logs to identify and analyze network anomalies and security events.
- Virtualization and Cloud Networking
-
- SDN (Software-Defined Networking): An approach to network management that allows dynamic, programmatically efficient network configuration.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): A private cloud environment within a public cloud infrastructure, providing isolated network resources.
Domain_04: Key Terms & Definitions
- Network Architecture and Design
- Network Topology: The arrangement of different elements (links, nodes, etc.) in a communication network (e.g., star, ring, mesh).
- OSI Model: A conceptual framework used to understand network interactions in seven layers (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application).
- TCP/IP Model: A set of communication protocols used for the Internet and similar networks. It has four layers (Link, Internet, Transport, Application).
- Secure Network Components
- Firewall: A network security device that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s previously established security policies.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): A device or software application that monitors a network for malicious activity or policy violations.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A service that creates a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet.
- Network Protocols and Security
- SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security): Protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers.
- IPSec (Internet Protocol Security): A protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol (IP) communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet in a data stream.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): An extension of HTTP used for secure communication over a computer network, widely used on the Internet.
- Secure Communication Channels
- Encryption: The process of converting information or data into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): A set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): A method of secure communication that prevents third-parties from accessing data while it’s transferred from one end system to another.
- Wireless Network Security
- WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3 (Wired Equivalent Privacy, Wi-Fi Protected Access): Security protocols and security certification programs developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): A unique ID that consists of 32 characters and is used for naming wireless networks.
- Network Attacks and Defenses
- DoS/DDoS (Denial of Service/Distributed Denial of Service): Attack attempts to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: A cyberattack where the attacker secretly intercepts and relays messages between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other.
- Packet Sniffing: The practice of using a network device to intercept and log traffic passing over a digital network or part of a network.
Domain_04: Key Areas
-
- Overview of Communication and Network Security
- Definition and importance in the context of CISSP
- Role in protecting information assets
- Overview of Communication and Network Security
-
- Network Architecture and Design
- Fundamental components (e.g., routers, switches, firewalls)
- Network topology types (star, mesh, hybrid, etc.)
- OSI and TCP/IP models
- Secure Network Components
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
- Firewalls and types (packet filtering, stateful, application-level)
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and their encryption methods
- Network Protocols and Security
- Common protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SSH, etc.)
- Protocol security mechanisms (SSL/TLS, IPSec)
- Risks and mitigation techniques
- Secure Communication Channels
- Ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability in data transmission
- Encryption standards and techniques (AES, RSA, ECC)
- Email and instant messaging security
- Wireless Network Security
- Wireless protocols (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC)
- Security concerns and protections (WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3)
- Best practices for wireless security
- Network Attacks and Defenses
- Common attack types (DoS/DDoS, Man-in-the-Middle, packet sniffing)
- Detection and prevention strategies
- Incident response and recovery
- Emerging Technologies and Trends
- Impact of IoT (Internet of Things) on network security
- Cloud networking and security implications
- Network Architecture and Design
Resources
Books Reference
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Study Guide (OSG) 9th Edition by Mike Chapple, James Michael Stewart, and Darril Gibson
- Chapter 11 – Chapter12, Pg495-635
- CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth Editionby Fernando Maymi and Shon Harris
- Part IV, Pg469-711
- Eleventh Hour CISSP® Study Guide, Third Editionby Eric Conrad, Seth Misenar, Joshua Feldma
- Domain-04, Pg95-116
- Destination Certification – A Concise Guideby Rob Witcher, John Berti, Lou Hablas, Nick Mitropoulos
- Domain-04, Pg241-312
-
The Official (ISC)2 CISSP CBK Reference, 6th Edition by Arthur Deane and Aaron Kraus
- Domain-04, Pg283-374
Practice Tests
- (ISC)2 CISSP Official Practice Testsby Mike Chapple and David Seidl
- How to Think Like a Manager for the CISSP Examby Luke Ahmed
- Boson Practice Exam
- Study Notes and Theory (SNT) by Luke Ahmed
Videos
- Mike Chapple’sCISSP Cert Prep on LinkedIn Learning.
- Kelly Handerhan’sCISSP Prep Course on Cybrary
- Destination CISSP Mindmap Video
- Pete Zerger’s CISSP Exam Cram
- Prabh’s Coffee Shots
- Luke Ahmed’s Study Notes and Theory (SNT)
Credits & Disclaimer
We express our gratitude to the below-mentioned authors, creators, and sources which have been referred for the creation of our Interactive CISSP Mindmap –Mike Chapple and David Seidl (OSG), Luke Ahmed (SNT), Pete Zerger (Exam Cram), Prashant Mohan (Memory Palace) , Prabh (Coffee shots), Rob Witcher (destcert.com/) and M. Waleed Khaliq (CISSP Concepts Guide).This Mindmap has been meticulously created to ensure that information is shared effectively. This Mindmap aims to offer a thorough grasp of essential concepts with a dedication to assist enhanced learning experiences. We hope that this resource helps people absorb information more thoroughly, which will lead to a broader understanding of each CISSP domains and is freely available for all.
Contribution
We have already included some reference images and short notes for most of the topics so that users can more effectively refer to the content in the mindmap. If you have any information, images, or notes that can make the mindmap more effective, please feel free to share them.
https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/tree/main/CISSP_Domain_04
For issues and concern please feel free to raise a issue in Github link https://github.com/sajinshivdas/CISSP_Interactive_Mindmap/issues
Connect with me www.linkedin.com/in/sajin-shivdas
Related Mindmaps
Find the related mindmaps of CISSP Domains below.